Abstract
Introduction IKZF1 (Ikaros) deletion has been related with poor outcome in pediatric B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (BCP ALL). However, its impact in adult patients (pts) treated with MRD-oriented trials has not been fully established. This study aimed to assess if IKZF1 deletions are markers of poor prognosis in adults with Ph-negative BCP ALL treated within the ongoing risk-adapted PETHEMA LAL19 trial (NCT04179929). The impact of IKZF1 loss in these pts and those from the EWALL Group (European Working group on ALL) is being evaluated in a HARMONY (Healthcare Alliance for Resourceful Medicine Offensive against Neoplasms in Hematology) project (Project Ref ALL2).
Methods In the PETHEMA LAL19 trial, pts with poor end-induction MRD clearance (MRD>0.01%) or high-risk genetics (low-hypodiploid, KMT2Ar, TP53 biallelic alteration or IKZF1+CDKN2A/B deletion) are assigned to allogeneic stem cell transplantation, the remaining pts receive maintenance chemotherapy. All pts are analyzed by G-banding, FISH, NGS (DNA gene panel) and SNP array. Next generation flow cytometry is used for MRD assessment.
Main outcome measures: i) Complete Remission (CR): absence of extramedullary disease, neutrophil level >1x109/L, platelet level >100x109/L, and bone marrow blast level < 5%; ii) Cumulative Incidence of Relapse (CIR) and non-relapse mortality (NRM): calculated using cumulative incidence rates to accommodate competing risks and compared by Gray's test; iii) Overall survival (OS): measured from the time of protocol entry to the time of death or last contact.
Results 147pts were analyzed. Mean age 40y [range 18-60], 56% males, 10% CNS involvement, 78% common B, 15% pro-B and 7% pre-B ALL. Ph-like (12%) was the most common genetic subtype followed by KMT2Ar (11%), PAX5 P80R (8%), low-hypodiploid (7%), TCF3::PBX1 and high-hyperdiploid (6% each), iAMP21 and ETV6::RUNX1 (2% each). More uncommon biological entities such as ZNF384r, MEF2Dr, MYCr, IDH1 R132C and IDH2 R140Q were seen in single pts (<1% each).The remaining patients (41%) were B-other,no growth or normal karyotype.
IKZF1 deletion (IK DEL) was observed in 66/147(45%) pts. Deletions involved the whole gene (37/66, 56%) or a subset of exons (partial gene deletions). The most recurrent partial gene deletions (n=29) were: loss of exons 4-7 (n=6, 21%), 4-8 (n=5, 17%), 2-8 and 1-7 (n=4, 14% each), 1-3 (n=3, 10%), 2&3 and 2-7 (n=2, 7% each). The IKZF1plus profile was observed in 37/147 (25%) pts. IK DEL were more frequent in low-hypodiploid (100%) and Ph-like ALL (88%), and less prevalent in KMT2Ar (19%), PAX5 P80R (18%) and TCF3::PBX1 ALL (11%), p<0.001.
Median follow up was 11.4 months. IKDEL pts showed lower CR rate than pts without Ikaros loss (75% vs. 91%, p=0.027). The IKZF1plus signature showed similar CR rate to IK DEL without IKZF1plus profile (IKZF1not plus) (73% vs. 78%, p=ns). IKDEL pts showed poorer MRD clearance than WT individuals. Interestingly, this fact was mainly attributable to partial gene deletions (MRD≥0.01% partial 79% vs. whole 42% vs. WT 29%, p=0.003). IKZF1plus was also correlated with positive MRD, however IKZF1not plus pts showed higher frequency of MRD positivity than IKZF1plus pts (MRD≥0.01% plus 47% vs. not plus 71% vs. WT 29%, p=0.012).
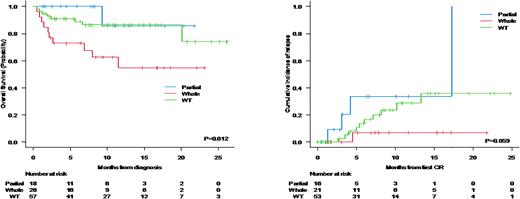
Pts with whole gene loss showed lower OS than pts with partial gene losses or IKZF1 WT (1y-OS 62% vs. 88% vs. 89%, p=0.012)(Figure 1A). Of note, relapse was not the main cause of death of IK DEL whole gene pts (n=26) as only 1 patient died due to disease progression. Instead, NRM was the main cause of death in whole gene-deleted pts (4 died in Ind-1, 3 in Ind-2, 1 due to TRM and 1 due to Covid19 infection). Accordingly, the 1y-CIR of IK DEL whole pts was lower than that of IKZF1 WT individuals, who showed similar CIR to IK DEL partial ones (1y-CIR whole 7% vs. WT 30% vs. partial 32%, p=0.059) (Figure 1B). Pts with IKZF1plus signature did not show differences in OS and CIR compared to IKZF1 WT or IKZF1not plus individuals (data not shown).
Conclusions This preliminary data suggest that IK DEL may be marker of poor treatment response in adult Ph-negative BCP ALL. Further analyses including all patients of the HARMONY project may identify which isoforms or in which genetic ALL subtypes IKZF1 DEL are particularly deleterious.
Disclosures
Hernández-Rivas:Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Research Support; Celgene/BMS: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Research support; Amgen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; GSK: Consultancy, Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.